Map 3D Measurements
This page describes Orbit generic 3D measure functions and the Map 3D main toolbar measure window to measure points, distances, lines, areas and volumes according the 3D Hover preference.
![]() Main Toolbar > Measure
Main Toolbar > Measure
More information about Map 2D and dedicated mobile mapping and oblique measurements see :
Measure Functions
Below, the generic Orbit 3D Measure functions.
Position
 Point
Point
Point measurement.
How to measure : measure single coordinate.
Result : xyz coordinate of measured point.
 Point height to ground
Point height to ground
Point measurement and height above approximate street surface1).
How to measure : measure point.
Results : xyz coordinate of measured point and height above approximate street surface.
 Point drop to ground
Point drop to ground
Point measurement dropped to approximate street surface and height above this surface.
How to measure : measure point.
Results : xyz coordinate of measured point dropped to approximate street surface and height above this surface.
 Point height to horizontal reference plane
Point height to horizontal reference plane
Point measurement and height above horizontal reference plane.
How to measure : (1) measure horizontal reference surface viaa single coordinate, (2) measure point.
Results : xyz coordinate of measured point and height above horizontal reference plane.
 Point drop to horizontal reference plane
Point drop to horizontal reference plane
Point measurement dropped to horizontal reference plane and height above this reference plane.
How to measure : (1) measure horizontal reference surface via single coordinate, (2) measure point.
Results : xyz coordinate of measured point dropped to horizontal reference plane and height above this plane.
Distance
 Distance XYZ
Distance XYZ
Distance measurement, straight line between 2 coordinates.
How to measure : measure 2 coordinates.
Results : xyz distance between measured points, slope and slant.
 Distance XYZ, XY and Z
Distance XYZ, XY and Z
Distance measurement, straight line between 2 coordinates.
How to measure : measure 2 coordinates.
Results : xyz, xy and z distance between measured points, slope and slant.
 Perpendicular distance to reference line
Perpendicular distance to reference line
Perpendicular distance measurement between a horizontal reference line and a point.
How to measure : (1) measure reference line as distance, (2) measure point.
Results : xyz, xy and z perpendicular distance between reference line and measured point, slope.
 Perpendicular distance to reference plane
Perpendicular distance to reference plane
Perpendicular distance measurement between a reference plane and a point.
How to measure : (1) measure reference plane via single coordinate, 3D hover will be used, (2) measure point.
Results : xyz distance and xyz coordinate of measured point.
Remarks : this measurement cannot be done via triangulation, point cloud required to measure 3D hover reference surface.
Line
 Free line
Free line
Poly-line measurement.
How to measure : (1) measure sequence of coordinates, (2) stop, see below.
Results : xyz, xy en z length.
 Catenary Curve
Catenary Curve
Catenary curve measurement.
How to measure : (1) measure start and end point as distance, (2) measure any point on catenary to define curve.
Results : Distance over curve, clearance and span.
Area
 Free area
Free area
Area measurement.
How to measure : (1) measure sequence of coordinates, (2) stop, see below.
Results : xyz, xy area and xyz, xy, z length.
 Vertical rectangular area
Vertical rectangular area
Vertical rectangular area measurement defined by 2 coordinates.
How to measure : (1) measure one corner as point, (2) measure diagonal opposite corner as point.
Results : xyz area.
 Horizontal rectangular area
Horizontal rectangular area
Horizontal rectangular area measurement defined by 3 coordinates.
How to measure : (1) measure one side as distance, (2) measure any point on the opposite side.
Results : xy area.
 Vertical rectangular area
Vertical rectangular area
Vertical rectangular area measurement defined by 3 coordinates.
How to measure : (1) measure one side as distance, (2) measure any point on the opposite side.
Results : xyz area.
Volume
 Rectangular volume
Rectangular volume
Rectangular volume measurement.
How to measure : (1) measure baseline as 2 points, (2) measure any point on the diagonal opposite baseline to finish measurement.
Results : Volume, baseline 1, baseline 2 and height.
How to measure
Measure and edit measurement
Once a measure function is activated or at completing the measurement the appearance of the mouse pointer indicates a coordinate can be added, replaced, removed or inserted :
- Left click elsewhere : add new coordinate for ongoing measurement according the 3D Hover preferences.
- Left click-and-drag elsewhere : standard Map 3D navigation
- Left click-and-drag measured coordinate : replace this coordinate according 3D Hover preferences.
- Left click measured segment : insert additional coordinate on the connecting segment between two measured coordinates
- Right click measured coordinate : delete this coordinate
- Right click-and-drag elsewhere : standard Map 3D navigation fuction
Stop measurement
Most measure functions do have a well known number of coordinates. These measurements will be finished automatically as soon the number expected measurement coordinates is completed.
Only for the “Free Line” and “Free Area” functions, the number of measured coordinates is not defined beforehand. These measurements can be ended by (a) a double left click or (b) a right click > “Stop measurement” once, respectively, at least 1 or 2 coordinates are measured. The ended position will be added as last measurement coordinate.
Use results
- Left click value
A single click on a displayed result value copies this value only to clipboard. - “Copy to clipboard”
Copy all displayed results (tab separated) to clipboard, ready to paste in a spreadsheet. - “Copy to Feature”
Copy measurement to the recorded dataset. This button is only enabled if the spatial object type (point,line,area) of the completed measurement and recorded dataset are the same.
Measure Results
Coordinate measurements
Absolute coordinates (xyz) are expressed in the Map coordinate system. If no vertical Map CRS is set, the Z of the used data source will be retained.
Relative measurements
Results depending Map CRS
Relative measurements (distance, line, area, volume) are expressed in the projected coordinate reference system as defined by Map CRS. If a geographical Map coordinate system is used, relative measurements will be calculated in an on-the-fly calculated local projection centered around the first measured coordinate. This local projections returns the most realistic metric result at all time.
Depending the projection parameters of the projected Map CRS or the origin of the on-the-fly created temporary projection the same “object measurement” will return different result values
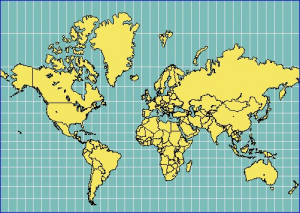
For example the Mercator projection conserves the angels, not the distances between different points. The distance increases closer to the poles. Have a look at the size of Greenland for example. It is about the same size as Saudi Arabia, about 2 million square kilometers.
Read more about the Coordinate reference systems and the supported systems here :
© Source image : http://www.heliheyn.de/Maps/GallPeters/GallPeters_E.html
Distance
- XYZ : 3D length of straight line between start and end point.
- XY : 2D length of straight line between start and end point, or length of the projected 3D distance with Z = 0.
- Z : absolute difference in Z between start and end point of straight line.
- Slope : The inclination with the horizontal reference plane expressed in % (100% = 45deg), also called grade.
- Slant : The inclination with the vertical reference plane expressed in degrees.
Length
- XYZ : Summed 3D length of each line segment as distance XYZ.
- XY : Summed 2D length of each line segment as distance XY.
- Z : Summed absolute difference in Z of each line segment as distance Z.
Catenary
- Distance over curve : 3D length over catenary curve
- Clearance : Minimum height above ground. The Ground height is calculated by the Z from the photo position minus the Heigt from the camera above the ground.
- Span : Distance XY.
Area
- XYZ : Area projected on best fit 3D plane through all measured vertices. This technique expects all vertices to be measured in approximately a single 3D plane.
- XY : 2D area, or area of projected 3D area with Z = 0.