This is documentation of an archived release.
For documentation on the current version, please check Knowledge Base.
For documentation on the current version, please check Knowledge Base.
Back to Dataset Legend Editor
Basic Appearance Rasters
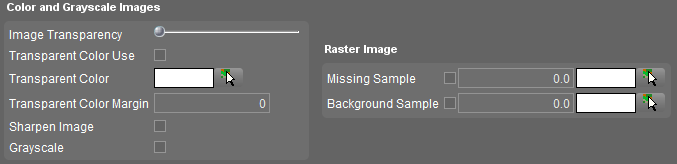
| Color and Gray-scale Images | ||
|---|---|---|
| Image Transparency | Set the transparency percentage of the image from opaque to completely transparent. | |
| Transparent Color | Transparent Color Use | Tick to activate the use of a transparent color in the image. |
| Transparent Color | Choose a color that should to be transparent. | |
| Transparent Color Margin | Enter the acceptable deviation (0-255) of an image pixel color from the chosen transparent color. | |
| Sharpen Image | See Wikipedia Unsharp masking. | |
| Grayscale | Set the color image to grayscale. | |
| Raster Image | ||
| Missing Sample | Checkbox | Tick to activate the use of a Missing Sample color in the image. |
| Value | Enter the value that represents the missing sample. | |
| Choose a color | Choose the color that displays the missing sample. | |
| Background Sample | Checkbox | Tick to activate the use of a Background Sample color in the image. |
| Value | Enter the value that represents the background sample. | |
| Choose a color | Choose the color that displays the background sample. | |
 The “Edit All Parameters” button is disabled, these are the only legend parameters to set for raster data.
The “Edit All Parameters” button is disabled, these are the only legend parameters to set for raster data.
Extra information about raster data
A raster consists of a matrix of cells (or pixels) where each cell contains a numerical value representing information, such as temperature, elevation,… . This numerical value allows to apply statistics and/or a classification to the dataset.
| Transparent Color | Instead of using a transparency for the whole image, it is possible to set only one color transparent. Generaly this is used for background colors (generaly black or white), or for pixels with no data. → A transparent color can be set to the missing sample color or background color. When the missing sample color and background sample color are the same, the transparent color can be set for both. → A transparent color is also used INSTEAD of a background sample color. |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
Without transparent color 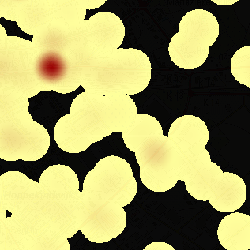 A classification 0 to 100 in ranges displayed in the image from yellow to red. To leave out all the data with no observed facts, the classification starts from 0.00001 instead of from 0. The zero-values are displayed in black. | Transparent color: Black  Black is used as a transparent color. |
|||
| Missing Sample | Every cell location in a raster has a value assigned to it. A cell is assigned the Missing Sample value if there is either no information or insufficient information about the characteristics of the location it represents. Be aware that the Missing Sample value and 0 are not the same, because 0 can be a valid value. → Example: missing sample value = -99999. |
|||
Classification  All valid values are displayed in a classification. The invalid values are displayed in black | Missing Sample: White 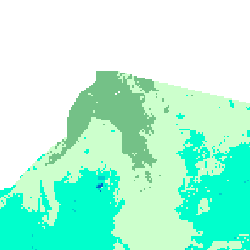 The invalid values (-9999) are displayed in white as a missing sample. |
|||
| Background Sample | Unlike the missing sample, the value of the background sample can be used in statistics and can be applied in the classification. The background sample value is a valid value, and mostly represents a standard- or startvalue. → Example: background sample value = 0. |
|||
Classification  A Classification: from 0 to 100 displayed in the image from yellow to red | Background Sample 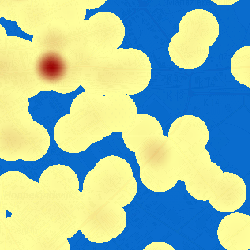 Value = 0 has been given a background color blue | Transparent color  The background color blue is set as a transparent color |
||
Last modified:: 2019/10/08 11:11