For documentation on the current version, please check Knowledge Base.
Georeference Data
The “Georeference ” tool can be used to position datasets missing a spatial reference on the Map 2D or 3D reference frame.
![]() Tools > … > Georeference
Tools > … > Georeference
Concepts
Georeferencing Aligning geographic data to a known coordinate system so it can be viewed, queried, and analyzed with other geographic data, using other data that is already georeferenced.
Georeferencing may involve shifting, rotating, scaling or skewing the data.
Reference data Spatial data that is already georeferenced, the CRS is known. Before starting georeferencing drag one or several georeferenced layers into the map view. It is important to use all the georeferenced available data to achieve a reasonable result. The more detailed and the more recent the information of reference data the better the result will be.
Control points Locations with known coordinates in the reference data, which have can be exactly identified in the resources to be georeferenced.
Mean fault measure of the differences between values predicted by a model or an estimator and the values actually observed. In our case differences between values in the reference dataset and the ones measured in the file to be georeferenced.
The Georeference Tab
- Open the file to be georeferenced
- Determining the control points happens in the Georeference Sidebar
Open file

Select the format according to the data you want to georeference:
- Image data or Vector data, all Supported Geodata Resources
- Point Cloud in Orbit format .OPC.
The file will open in the the Georeference Tab.
Navigation Tools
Tools designed to help navigating in the georeferencing window : Pan, Zoom, Previous/Next view, Select
More info about navigating in the map view : Mapcanvas navigation
Backdrop color
Togle betwen several colors for the Georeference Tab. Useful for displaying white or pale color resources.
Sidebar
The Sidebar evaluates corresponding points on the reference map ( Orbit Map Canvas ) and the new image, vector file and pointcloud ( in the Georeference Tab).
File Type
Choose what type of data you want to georeference : imagery, vector data or pointclouds.
The pointcloud must be in a projected coordinate system.
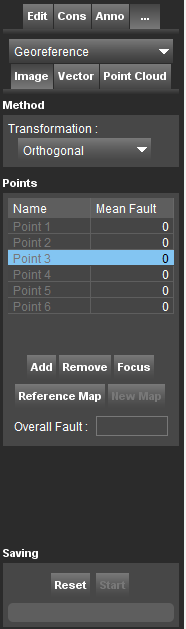
Method
Transformation
Select the mathematical method to use for georeferencing.
For imagery and vectors choose between: Orthogonal, Affine, Translate and Scale, Translate.
For pointclouds choose between: XYZ translation, XY translation, Z translation and generic.
Points
In order to define the Control Points, measure a point on the reference map by clicking a position. Do the same on the new image/vector.
When 3 corresponding points are measured, Orbit calculates a mean fault. At least 3 points must be measured.
Add Row/Remove
Gives the possibility to measure additional points or removes a measurement.
Focus
Focus the map on the selected point location.
Reference Map
If enabled, the active map to measure is the Map Canvas.
New Map
If enabled, the active map to measure is the Georeference Tab.
Overall Fault
To improve georeference, keep the overall fault as low as possible.The overall mean fault should be lower than 0.2. If higher: find the point with the largest fault, edit its measurement and recalculate.
Saving
Start
Press to calculate the georeferencing. This will save the georeference information to a worldfile in case of an image , and to an .ORD file for vectors or pointclouds. The georeferenced file will be added to the Orbit workspace.
Reset
Reset will delete all the measurements (reference points) existent in the reference data and in the new resource.
Examples
Imagery
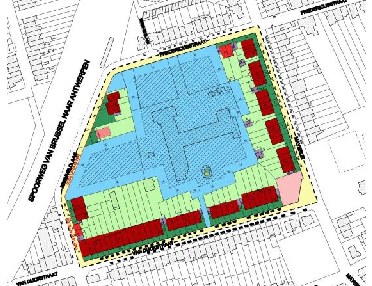
Consider the georeferenced context and the image who has to be georeferenced (for example an aerial image)

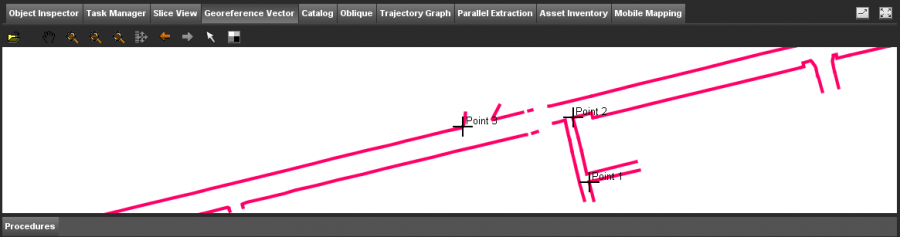
Open the Georeference Calculation Window to determine the controle points.
Search a location in one of both views of which you are able to define the exact same location in the other view. Click in the measure-button in the reference column and point out this specific location in the georeferenced context. The same location will be pointed out with the measure-button in the new image column.
Find at least 3 of such location to be able to georeference the image.

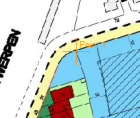

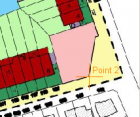

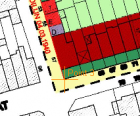
When 2 points are calculated the exact scale can be measured. From the third point on the distortion on this scale is calculated. This is the error visible in the right corner.
The quality of georeferencing will increase if:
- The control points are not chosen on one line
- control points are spread over the image
Pointcloud
It is possible to georeference a pointcloud using:
- Another point cloud
- A vector file
To use values from .csv,.dbf or .txt files as control points, the user must first import those files as a vector files, and only then start the georeference procedure.
The worldfile
A new textfile with the georeference details will be made and saved under the same path as the location of the georeferenced image. This textfile, which is named a worldfile contains 6 numbers:
- Line 1: pixelsize in the x-direction in map units
- Line 2: rotation about y-axis
- Line 3: rotation about x-axis
- Line 4: pixelsize in the y-direction in map units
- Line 5: x-coordinate of the center of the upper left
- Line 6: y-coordinate of the center of the upper left
Source: Wikipedia
Deleting this file will delete the georeference.
For different resources, the wordfile will have different extensions :
- For .omi images the worldfile will have the extension .oiw
- For .tif images the worldfile will have the extension .tfw
- For .jpg images the worldfile will have the extension .jgw
- For .png images the worldfile will have the extension .pgw
- For .ers images the worldfile will have the extension .esw
- For .oif images the worldfile will have the extension .ofw
- For .bmp images the worldfile will have the extension .bpw